learning System design as a landscape architect 7
Rethink system design in a much fun way, as a former urban planner/landscape planner. Take Collaborative Editing System as example
- Collaborative Editing System
Collaborative Editing System
Google Docs
Scenario analysis
basic function
- What is the main function of documentation editor(word)
- New/Load File
- Edit File
- Save File
- What is the main function of Collaborative Editor (Google Docs)
- Collaboration
- Display Co-Authoring
- Who updat
- Content lock
HTTP 1.0
- don’t support Long Connection
- Three-way Hand
- Slow Star
- TCP Connection
- Head of Line Blocking
HTTP 1.1
- dsupport Long Connection
- one TCP Connection: mutiple Request + Response
- Pipeline
Neither HTTP1.0 nor HTTP1.1 can send data from the server to the client.
WebSocket can communicate in both directions (server and client).
WebSocket
- build up connection
- keep the session
- update the content
Features
- Support two-way communication
- Strong real-time performance The server actively sends requests to the client, which solves the real-time problem
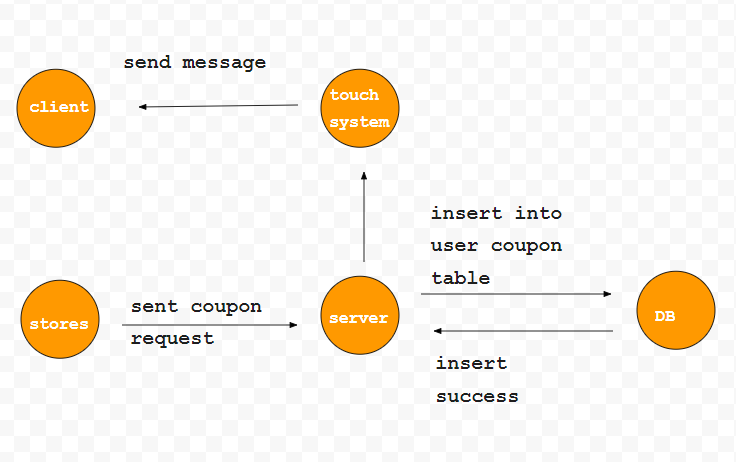
stock system
Service analysis
request files
URL design
You cannot use http://xxx.com/aa/bb/cc.mp4 when sharing this file, because of safty reason and the links is too long for sharing.
Generate a unique key or uuid for each file.
improve the readability
add file slugify string as suffix
simple file request process
Clint –1. Request URL –> Web Server – 2. Locate File –> File System
File System –3. Get File –> Web Server – 4. Response –> Clint
save files
Metadata & Content
- Metadata –> DB
- key
- filename
- size …
- Content –> File System
file operation
basic file operation: CRUD
Granularity: what if take the whole file as Granularity?
improve:
use a row as Granularity,
use a word as Granularity: google docs
save struture
LRU CACHE
conbine quick search(hashset) and quick insert/remove (LinkedNode)
-
If we add elements from the tail of the linked list by default, then obviously the elements closer to the tail are the most recently used, and the elements closer to the head are the ones that have not been used for the longest time.
-
For a certain key, we can quickly locate the node in the linked list through the hash table to obtain the corresponding val.
-
The linked list obviously supports fast insertion and deletion at any position, just change the pointer. It’s just that the traditional linked list cannot quickly access an element at a certain position according to the index, but here with the help of the hash table, you can quickly map to any linked list node through the key, and then insert and delete.
why doubly linked list
• It is stored as a specific file on the file server • The application server is loaded from the file server, and the content of the file is stored in memory • Advantages of linked list Insert or delete at any position, good performance • Each line of data in the file matches a node in the linked list • Changes in content are equivalent to changes in linked list nodes
How to convert the file into a linked list
aa.txt
aaaaaaa
bbbbbbb
ccccc
...
Each row is a struct Key: Unique identifier for each line of the file Value: the content of each row preId: predecessor Id, the previous line afterId: follow-up Id, next line
Frontend generate the key and the uuid of each row when the front-end page is rendered and record it.
key(uuid) value preId afterId
00 aaaaaaa 11
11 bbbbbbb 00 22
22 ccccc 11 ..
modify content
What information needs to be sent to the server when adding or changing content on the front end
edit files
create file data flow
Client –1. create file request–> Web Server
Web Server –2. transfer the created file–> File Server
Web Server –3. save Metadata–> MySQL DB
File Serve –4. save file–> File System
edit file data flow
Client –1. edit file –> Web Server
Web Server –2. save the modified part–> Redis –> Scheduled Task
Web Server –3. update Metadata–> MySQL DB
Scheduled Task –4. combine modify–> File Server
File Server –5. save file–> Distributed File System
When editing, the changed content is saved in Redis as linked list + hash table, and writes asynchronously to the file server.
Table
MySQL
fileid filename fileURL filesurfix
Redis contains 2 keys, one records head and tail; one records each row content after modifying.
Key: file key
Value: {
dummy: string;
tail: string;
}
Key: file key + row key
Value: {
content: string;
preID: string;
nextID: string;
}
add new row
aa.txt
aaaaaaa
bbbbbbb
<!-- add new row -->
eee
ccccc
...
key(uuid) value preId afterId
00 aaaaaaa 11
11 bbbbbbb 00 99
99 eee 11 11
22 ccccc 99 ..
How to guarante mutiple users generate the same uuid when operating on the same row
modify new col
aa.txt
aaaaaaa
bbbbxxx
<!-- add new row -->
eee
ccccc
...
key(uuid) value preId afterId
00 aaaaaaa 11
11 bbbbxxx 00 99
99 eee 11 11
22 ccccc 99 ..
Collaborative Editin
display avatars edited by multiple people at the same time
user lists saved in NoSQL (The data information of the user list is frequently changed)
display avater data flow
user 1 : –1. Update while editing user list –> server
user 2 : –1. Update while editing user list –> server
server : –2. query user information –> user list
server : –3. save the file when editing user list –> user list
display who is editing the row
user 1 – when editing upload user id and row id–> server
server – synchronic data to user 2–> user 2
server —-> Redis key:value< row id : user id>
What cases may be encountered when multiple users edit at the same time?
-
Multiple people editing a row at the same time
-
One is deleting a row, one is adding
Simultaneous locking, Decide who to adopt by the time it arrives at the server
Or use two methods no need lock.
- OT(Operational Transform) –> Google Docs
- CRDT(Conflict-Free Repicated Data Type)