learning System design as a landscape architect 11
Rethink Location Based Service system design in a much fun way, as a former urban planner/landscape planner. Take Uber as example
System Design = Logic Design(why) + Infrastructure Design(how)
Design UBER
Scenario analysis
Functional Requirement
- Driver report location
- Rider request Uber, match a driver with rider
Second step:
- Rider cancel a request
- Driver deny / accept a request
- Driver cancel a request
- Driver pick up a rider
- Driver drop off a rider
data
2022 2 million drivers in Uber (google)
assume Peak Driver QPS = 300 k
Storage acculation
-
assume every location data: 600 k * 86400 / 4 * 100 bytes ~ 1.3 T (Driver report locations by every 4 seconds)
-
assume only store current location data: 600 k * 100 bytes = 60 M 1 M = 10^6 bites
Service
- GeoServer (record locations)
- DispatchServer
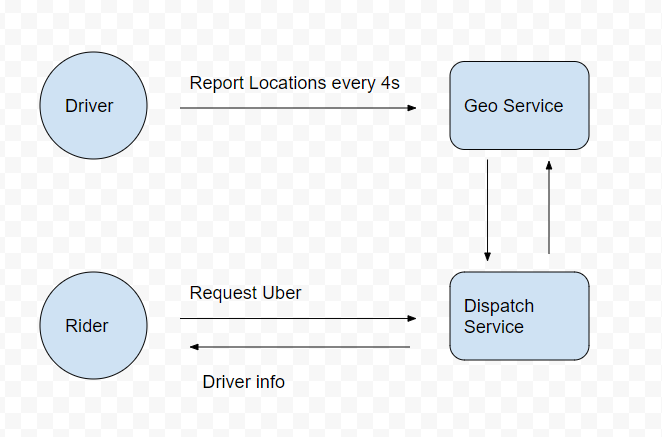
Geo/Dispatch Service
How Drivers receive Riders' request
Report location, at the same time, the Service return matched request
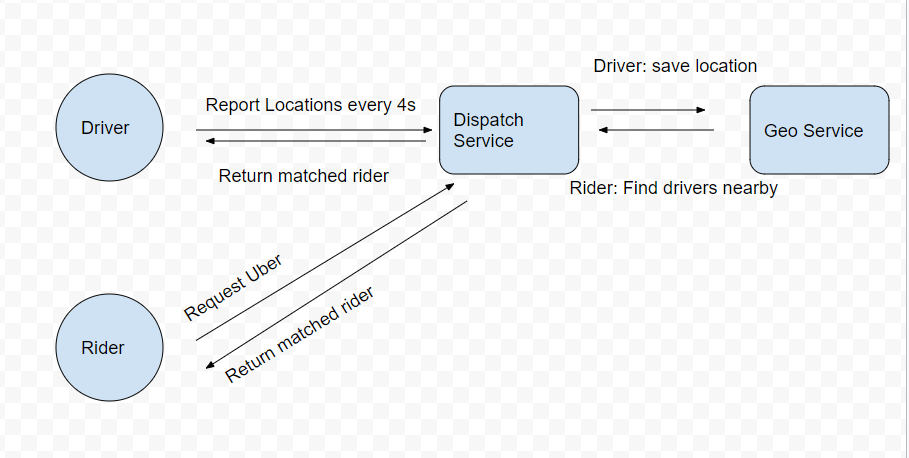
Geo/Dispatch Service
Storage
Dispatch Web Server –> Trip Table
Geo Web Server –> Location Table
Consider read/write frequency on a database table?
Schema
Trip Class
class Trip {
public Integer tripId;
public Integer driverId, riderId;
public Double startLatitude, startLongitude;
public Double endLatitude, endLongitude;
public Integer status;
public Datetime createAt;
}
Trip Table type comments
//
status int New request / waiting for driver / on the way to pick up / in trip / cancelled / ended
Location Class
class Location {
public Integer driverId;
public Double Latitude, Longitude;
public Datetime updateAt;
}
Location Table type comments
driver_id fk Primary key
lat float
lng float
updated_at timestamp
Trip Class is a heavily read database, and Location class is the opposite
save and query location info
how to search nearby drivers
query the lat and lng from Location table, inorder to improve the query process, The lat and lng statement are used to create indexes in tables.
create composite index lat_lng_idx on location_table ?
actually, composite index can only be used in accurate lat value and certain range of lng.
[111, 300] ~ [111, 400]
The index of the database can only solve one dimension Range Query.
Range Query with multiple dimensions cannot be efficiently queried.
Search for vehicles within a 2km radius use geohash in database
according to the geohash length, eg: find all vehicles start with 9q9jv
Storage (geohash)
SQL
- CREATE INDEX on geohash
- SELECT * FROM location WHERE geohash LIKE
9q9hv%
NoSQL (Cassandra)
- set geohash as column key
- range query (9q9hv0, 9q9hvz)
NoSQL (Redis)
-
storing Driver Location data hierarchy in redis
- Driver locatoin is
9q9hvt, then store it in9q9hvt,9q9hv,9q9h - geohash of length
6produces cells that cover less than a square1 kilometerof land, which is enough for Uber - geohash of length
4produces cells that cover more than a square20 kilometerof land
- Driver locatoin is
-
key = 9q9hvt, value = set of drivers in this location
NoSQL (Redis) as database
support list, set, remove in set is O(1).
Read and write speed close to memory access speed >100k QPS.
data flow between riders and drivers
Riders' request for drivers
- User makes a taxi request to find drivers around a given location
- (lat,lng) → geohash → [driver1, driver2,…]
- Check the 6-digit geohash to find the one within 0.6 km
- If there is no reply, then check the 5th geohash to find the one within 2.4 km
- If there is no reply, then check the 4-digit geohash ༌ to find the one within 20 kilometers
Location Table
key geohash
value {driver1_id, driver2_id, driver3_id..}
- The driver is successfully matched, and the user queries the location of the driver
Driver Table
key driver_id
value (lat, lng, status, updated_at, trip_id)
Drivers data from in database
-
Drivers report their location
- Calculate the geohash of the current location lat, lng
- geohash4, geohash5, geohash6
- query old location
- updates in the Redis
- updates their latest active time in Driver Table
- Calculate the geohash of the current location lat, lng
-
Drivers accepty the riders request
- edit the Trip status
- when a riders sends request, Trip Table creates a trip and matches the closest driver.
- update their status as nonavailable in Driver Table
- edit the Trip status
-
Driver complete the trip
- edit the Trip status
- update their status as available in Driver Table
data flow
-
Rider make requests, server create a trip
- return
trip_idto rider - send requests every few seconds to the server to check the match
- return
-
server find the matched driver, write to the trip, waiting for the driver’s response
- update the
driver's statusas nonavailable, save in the related trip_id
- update the
-
drivers report their location
- find the
trip_idinDriver table - query the trip in
trip table, return to the driver
- find the
-
driver accept the request
- update the status info in
Driver Table,Trip table - rider finds the match, get driver’s info
- update the status info in
-
driver rejuect the request
- update the status info in
Driver Table,Trip table - server rematch a new driver, repeat step 2
- update the status info in
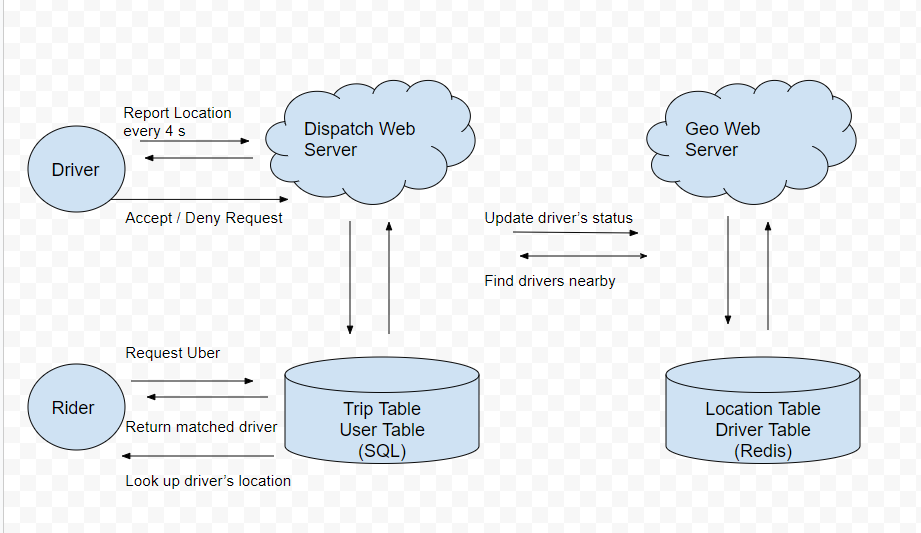
Geo/Dispatch Service
Scale
demand: 300 QPS
Redis is good choice for > 100 QPS. So we need 3-4 Redis server?
Interviewer: one Redis server is crash?
DB Sharding
- Distributing incoming network traffic
- Avoiding Single Point Failure
how to shard
- sharding is based on the first 4 length Geohash
- query is based on the 4-6 length geohash numbers
or sharding by cities (geo fence)
Interviewer: How to check rider is in Airport
create a geofence around a city then create a geofence arround airport.
Interviewer: How to reduce impact on db crash?
method 1: Redis Master Slave
write to the Master server, but slave server the reduce the read traffic.
method 2: better NoSQL database choice
ig: 300k QPS, use 1000 Cassandra –the average QPS of 300 per unit.
It will help you better deal with Replica and recovery after a crash.
